Rhind Mathematical Papyrus
| Rhind Mathematical Papyrus | |
|---|---|
| British Museum, London | |
A portion of the Rhind Papyrus |
|
| Date | Second Intermediate Period of Egypt |
| Place of origin | Thebes |
| Language(s) | Hieratic |
| Size | Length: 199.5 centimetres (78.5 in) Width: 32 centimetres (13 in) |
| Other | BM/Big no. AE 10058, Reg no. 1865,0218.3 |
The Rhind Mathematical Papyrus (RMP) (also designated as: papyrus British Museum 10057, and pBM 10058), is named after Alexander Henry Rhind, a Scottish antiquarian, who purchased the papyrus in 1858 in Luxor, Egypt; it was apparently found during illegal excavations in or near the Ramesseum. It dates to around 1650 BC. The British Museum, where the papyrus is now kept, acquired it in 1864 along with the Egyptian Mathematical Leather Roll, also owned by Henry Rhind;[1] there are a few small fragments held by the Brooklyn Museum in New York[2]. It is one of the two well-known Mathematical Papyri along with the Moscow Mathematical Papyrus. The Rhind Papyrus is larger than the Moscow Mathematical Papyrus, while the latter is older than the former.[2]
The Rhind Mathematical Papyrus dates to the Second Intermediate Period of Egypt and is the best example of Egyptian mathematics. It was copied by the scribe Ahmes (i.e., Ahmose; Ahmes is an older transcription favoured by historians of mathematics), from a now-lost text from the reign of king Amenemhat III (12th dynasty). Written in the hieratic script, this Egyptian manuscript is 33 cm tall and just under 2 m long, and began to be transliterated and mathematically translated in the late 19th century. In 2008, the mathematical translation aspect is incomplete in several respects. The document is dated to Year 33 of the Hyksos king Apophis and also contains a separate later Year 11 on its verso likely from his successor, Khamudi.[3]
In the opening paragraphs of the papyrus, Ahmes presents the papyrus as giving "Accurate reckoning for inquiring into things, and the knowledge of all things, mysteries...all secrets". He continues with:
This book was copied in regnal year 33, month 4 of Akhet, under the majesty of the King of Upper and Lower Egypt, Awserre, given life, from an ancient copy made in the time of the King of Upper and Lower Egypt Nimaatre (?). The scribe Ahmose writes this copy.[1]
Several books and articles about the Rhind Mathematical Papyrus have been published, and a handful of these stand out.[2] The Rhind Papyrus was published in 1923 by Peet and contains a discussion of the text that followed Griffith's Book I, II and III outline [4] Chase published a compendium in 1927/29 which included photographs of the text.[5] A more recent overview of the Rhind Papyrus was published in 1987 by Robins and Shute. [6]
Contents |
Book I
The first part of the Rhind papyrus consists of reference tables and a collection of 20 arithmetic and 20 algebraic problems. The problems start out with simple fractional expressions, followed by completion (sekhem) problems and more involved linear equations (aha problems).[2]
The first part of the papyrus is taken up by the 2/n table. The fractions 2/n for odd n ranging from 3 to 101 are expressed as sums of unit fractions. For example 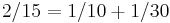 . The decomposition of 2/n into unit fractions is never more than 4 terms long as in for example
. The decomposition of 2/n into unit fractions is never more than 4 terms long as in for example 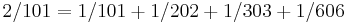 .
.
This table is followed by a list of fraction expressions for the numbers 1 through 9 divided by 10. For instance the division of 7 by 10 is recorded as:
- 7 divided by 10 yields 2/3 + 1/30
After these two tables, the scribe recorded 84 problems altogether and problems 1 through 40 which belong to Book I are of an algebraic nature.
Problems 1–6 compute divisions of a certain number of loaves of bread by 10 men and record the outcome in unit fractions. Problems 7–20 show how to multiply the expressions 1 + 1/2 + 1/4 and 1 + 2/3 + 1/3 by different fractions. Problems 21–23 are problems in completion, which in modern notation is simply a subtraction problem. The problem is solved by the scribe to multiply the entire problem by a least common multiple of the denominators, solving the problem and then turning the values back into fractions. Problems 24–34 are ‘’aha’’ problems. These are linear equations. Problem 32 for instance corresponds (in modern notation) to solving x + 1/3 x + 1/4 x = 2 for x. Problems 35–38 involve divisions of the hekat. Problems 39 and 40 compute the division of loaves and use arithmetic progressions.[1]
Book II
The second part of the Rhind papyrus consists of geometry problems. Peet referred to these problems as "mensuration problems". [2]
Volumes
Problems 41 – 46 show how to find the volume of both cylindrical and rectangular based granaries. In problem 41 the scribe computes the volume of a cylindrical granary. Given the diameter (d) and the height (h), the volume V is given by:
In modern mathematical notation (and using d = 2r) this clearly equals 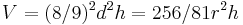 The quotient 256/81 approximates the value of π as being ca. 3.1605.
The quotient 256/81 approximates the value of π as being ca. 3.1605.
In problem 42 the scribe uses a slightly different formula which computes the volume and expresses it in terms of the unit khar. 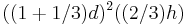 In modern mathematical notation this is equal to
In modern mathematical notation this is equal to 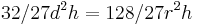 (measured in khar). This is equivalent to
(measured in khar). This is equivalent to 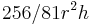 measured in cubic-cubits as used in the other problem. [1]
measured in cubic-cubits as used in the other problem. [1]
Problem 47 gives a table with equivalent fractions for fractions of 100 quadruple hekat of grain. The quotients are expressed in terms of Horus eye fractions. The short table gives the values related to the original 100 quadruple hekat:
- 1/10 gives 10 quadruple hekat
- 1/20 gives 5 quadruple hekat
- 1/30 gives 3 1/4 1/16 1/64 (quadruple) hekat and 1 2/3 ro
- 1/40 gives 2 1/2 (quadruple) hekat
- 1/50 gives 2 (quadruple) hekat
- 1/60 gives 1 1/2 1/8 1/32 (quadruple) hekat 3 1/3 ro
- 1/70 gives 1 1/4 1/8 1/32 1/64 (quadruple) hekat 2 1/14 1/21 ro
- 1/80 gives 1 1/4 (quadruple) hekat
- 1/90 gives 1 1/16 1/32 1/64 (quadruple) hekat 1/2 1/18 ro
- 1/100 gives 1 (quadruple) hekat[1]
Areas
Problems 48 - 55 show how to compute an assortment of areas. Problem 48 is often commented on as it computes the area of a circle. The scribe compares the area of a circle (approximated by an octagon) and its circumscribing square. Each side is trisected and the corner triangles are then removed. The resulting octagonal figure approximates the circle. The area of the octagonal figure is: ![9^2 - 4 \times [\frac{1}{2}(3)(3)] = 63](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/dd2eb68e094598e949b504228049f86e.png) ; Next we approximate 63 to be 64 and note that
; Next we approximate 63 to be 64 and note that 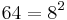 . And we get the approximation
. And we get the approximation 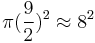 . Solving for π, we get the approximation
. Solving for π, we get the approximation 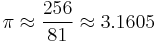 (the approximation has an error of .0189).
(the approximation has an error of .0189).
That this octagonal figure, whose area is easily calculated, so accurately approximates the area of the circle is just plain good luck. Obtaining a better approximation to the area using finer divisions of a square and a similar argument is not simple. [1][7] Other problems show how to find the area of rectangles, triangles and trapezoids.
Pyramids
The final five problems are related to the slopes of pyramids. A seked problem is reported by :[8]
- If a pyramid is 250 cubits high and the side of its base 360 cubits long, what is its seked?"
The solution to the problem is given as the ratio of half the side of the base of the pyramid to its height, or the run-to-rise ratio of its face. In other words, the quantity he found for the seked is the cotangent of the angle to the base of the pyramid and its face.[8]
Book III
The third part of the Rhind papyrus consists of a collection of 24 problems. [2] Problem 61 consists of 2 parts. Part 1 contains multiplications of fractions. Part b gives a general expression for computing 2/3 of 1/n, where n is odd. In modern notation the formula given is
Problems 62- 68 are general problems of an algebraic nature. Problems 69 - 78 are all pefsu problems in some form or another. They involve computations regarding the strength of bread and or beer. [1]
Problem RMP 79' sums five terms in a geometric progression. It is a multiple of 7 riddle, which would have been written in the Medieval era as, "Going to St. Ives" problem.[2] Problems 80 and 81 compute Horus eye fractions of henu (or hekats). Problem 81 is followed by a table. The last three problems 82 - 84 compute the amount of feed necessary for fowl and oxen. [1]
See also
- Lahun Mathematical Papyri
- Akhmim wooden tablet
- Berlin Papyrus also known as Berlin Papyrus 6619
- Rhind Mathematical Papyrus 2/n table
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h Clagett, Marshall Ancient Egyptian Science, A Source Book. Volume Three: Ancient Egyptian Mathematics (Memoirs of the American Philosophical Society) American Philosophical Society. 1999 ISBN 978-0-87169-232-0
- ^ a b c d e f g Anthony Spalinger , The Rhind Mathematical Papyrus as a Historical Document, Studien zur Altägyptischen Kultur, Bd. 17 (1990), pp. 295-, Helmut Buske Verlag GmbH
- ^ cf. Thomas Schneider's paper 'The Relative Chronology of the Middle Kingdom and the Hyksos Period (Dyns. 12-17)' in Erik Hornung, Rolf Krauss & David Warburton (editors), Ancient Egyptian Chronology (Handbook of Oriental Studies), Brill: 2006, p.194-195
- ^ Peet, Thomas Eric. 1923. The Rhind Mathematical Papyrus, British Museum 10057 and 10058. London: The University Press of Liverpool limited and Hodder & Stoughton limited
- ^ Chace, Arnold Buffum. 1927-1929. The Rhind Mathematical Papyrus: Free Translation and Commentary with Selected Photographs, Translations, Transliterations and Literal Translations. Classics in Mathematics Education 8. 2 vols. Oberlin: Mathematical Association of America. (Reprinted Reston: National Council of Teachers of Mathematics, 1979). ISBN 0-87353-133-7
- ^ Robins, R. Gay, and Charles C. D. Shute. 1987. The Rhind Mathematical Papyrus: An Ancient Egyptian Text. London: British Museum Publications Limited. ISBN 0-7141-0944-4
- ^ Don Allen Egyptian and Babylonian Mathematics from [1]
- ^ a b Maor, Eli (1998). Trigonometric Delights. Princeton University Press. p. 20. ISBN 0691095418.
Further reading
- Gillings, Richard J. "Mathematics in the Time of the Pharaohs", 1972, MIT Press, Dover reprint ISBN 0-486-24315-X
External links
- Allen, Don. April 2001. The Ahmes Papyrus and Summary of Egyptian Mathematics.
- Egypt/Texts at the Open Directory Project
- British Museum webpage on the Papyrus.
- O'Connor and Robertson, 2000. Mathematics in Egyptian Papyri.
- Truman State University, Math and Computer Science Division. Mathematics and the Liberal Arts: The Rhind/Ahmes Papyrus.
- "Rhind Papyrus". MathWorld–A Wolfram Web Resource. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/RhindPapyrus.html.
- Williams, Scott W. Mathematicians of the African Diaspora, containing a page on Egyptian Mathematics Papyri.
- BBC audio file A History of the World in 100 Objects. (15 mins)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
![V = [(1-1/9) d]^2 h](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/89ed40de3759aa87c30c71469f915d2d.png)